Glossitis
Glossitis refers to an inflamed tongue. The tongue becomes red, sore and swollen. The papillae of the tongue atrophy (shrink), giving the tongue a smooth appearance. It is sometimes described as “beefy”.
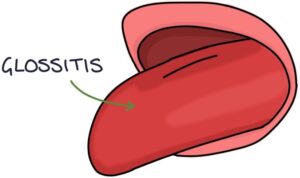
Causes:
- Iron deficiency anaemia
- B12 deficiency
- Folate deficiency
- Coeliac disease
- Injury or irritant exposure
Management involves correcting the underlying cause.
Angioedema
Angioedema refers to fluid accumulating in the tissues, resulting in swelling. It can affect a number of areas, such as the limbs, face and lips. It can affect the tongue, causing the tongue to swell.
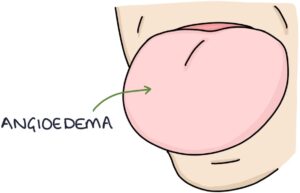
The three top causes of angioedema to remember for exams are:
- Allergic reactions
- ACE inhibitors
- C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency (hereditary angioedema)
Oral Candidiasis
Oral candidiasis is also called oral thrush. It refers to an overgrowth of candida, a type of fungus, in the mouth. This results in white spots or patches that coat the surface of the tongue and palate.
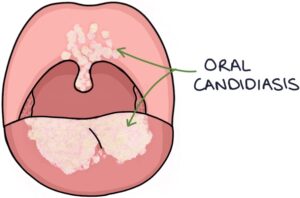
Several common factors can predispose someone to develop oral candidiasis:
- Inhaled corticosteroids (particularly with poor technique, not using a spacer and not rinsing with water afterwards)
- Antibiotics (disrupt the normal bacterial flora giving candida a chance to thrive)
- Diabetes
- Immunodeficiency (consider HIV)
- Smoking
Treatment options are:
- Miconazole gel
- Nystatin suspension
- Fluconazole tablets (in severe or recurrent cases)
Geographic Tongue
Geographic tongue is an inflammatory condition where patches of the tongue’s surface lose the epithelium and papillae. The patches form irregular shapes on the tongue, resembling a map, with countries and oceans bordering each other.
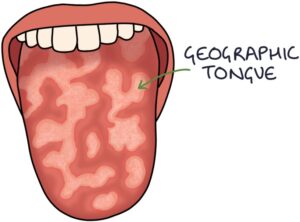
The condition tends to relapse and remit, with episodes of the abnormal tongue appearance that can last days to weeks before resolving or changing. The cause of these changes is not known.
Geographic tongue often occurs without any associations. However, it can be related to:
- Stress and mental illness
- Psoriasis
- Atopy (asthma, hayfever and eczema)
- Diabetes
Geographic tongue is a benign condition and does not cause any harmful effects. It does not usually require any treatment. Symptoms such as discomfort or burning are sometimes treated with topical steroids or antihistamines.
Strawberry Tongue
A strawberry tongue appearance occurs when the tongue becomes swollen and red, and the papillae become enlarged, white and prominent.
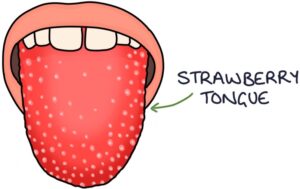
The two key causes of a strawberry tongue to remember are:
- Scarlet fever
- Kawasaki disease
Black Hairy Tongue
Black hairy tongue results from decreased shedding (exfoliation) of keratin from the tongue’s surface. The papillae elongate and take on the appearance of hairs. Bacteria and food cause the dark pigmentation. This gives the appearance of black hair on the tongue. Patients may also report sticky saliva and a metallic taste.
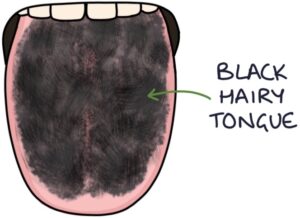
Black hairy tongue may be due to dehydration, a dry mouth, poor oral hygiene and smoking.
Management involves ensuring adequate hydration, gentle brushing of the tongue and stopping smoking.
Last updated July 2021
Now, head over to members.zerotofinals.com and test your knowledge of this content. Testing yourself helps identify what you missed and strengthens your understanding and retention.

