Cataracts describe a progressively opaque eye lens, which reduces the light entering the eye and visual acuity.
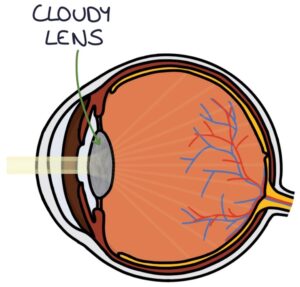
The role of the lens is to focus light on the retina. It is held in place by suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary body. The ciliary body contracts and relaxes to change the shape of the lens. When the ciliary body contracts, it releases tension on the suspensory ligaments, and the lens thickens. When the ciliary body relaxes, the suspensory ligaments tension, and the lens narrows. The lens has no blood supply and is nourished by the aqueous humour.
Most cataracts take years to develop. Congenital cataracts occur before birth. The red reflex is tested during the neonatal examination to screen for congenital cataracts.
Risk Factors
- Increasing age
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Diabetes
- Steroids
- Hypocalcaemia
Presentation
Symptoms are usually asymmetrical, as both eyes are affected separately. It presents with:
- Slow reduction in visual acuity
- Progressive blurring of the vision
- Colours becoming more faded, brown or yellow
- Starbursts can appear around lights, particularly at night
Loss of the red reflex is a key examination finding. The lens can appear grey or white using an ophthalmoscope, even from a distance. This is also seen on photographs taken with a flash.
Management
No intervention may be necessary if the symptoms are manageable.
Cataract surgery involves drilling and breaking the lens to pieces, removing the pieces and implanting an artificial lens. It can be performed as a day case under local anaesthetic and generally gives good results.
Cataracts can prevent the detection of other pathology, such as macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy, which can become apparent after surgery. Therefore, they may still have reduced visual acuity after the cataract is treated.
Endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis describes inflammation of the inner contents of the eye, usually caused by infections, and is a rare but serious complication of cataract surgery. It can lead to vision loss. It is treated with intravitreal antibiotics injected directly into the eye.
Last updated October 2023
