Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is an inherited disease that affects the peripheral motor and sensory neurones. It is also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy. There are various types, with different genetic mutations and pathophysiology, causing myelin or axon dysfunction. The majority of mutations are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Symptoms usually start to appear before the age of 10 but can be delayed until 40 or later.
Classical Features
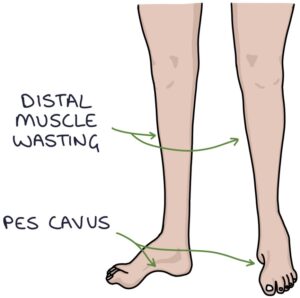
There are some classical features of Charcot-Marie-Tooth. Not all of these features will apply to all patients:
- High foot arches (pes cavus)
- Distal muscle wasting causing “inverted champagne bottle legs”
- Lower leg weakness, particularly loss of ankle dorsiflexion (with a high stepping gait due to foot drop)
- Weakness in the hands
- Reduced tendon reflexes
- Reduced muscle tone
- Peripheral sensory loss
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy refers to reduced sensory and motor function in the peripheral nerves, typically affecting the feet and hands (“stocking-glove” distribution). It is a characteristic feature of Charcot-Marie-Tooth.
Other causes of peripheral neuropathy can be remembered with the ABCDE mnemonic:
- A – Alcohol
- B – B12 deficiency
- C – Cancer (e.g., myeloma) and Chronic kidney disease
- D – Diabetes and Drugs (e.g., isoniazid, amiodarone, leflunomide and cisplatin)
- E – Every vasculitis
TOM TIP: A common OSCE scenario is to examine a patient with peripheral neuropathy. Charcot-Marie-Tooth is a relatively common condition with good signs and stable patients, making it popular in OSCEs. Look for the other features of the condition, suggest the diagnosis, and then run through the ABCDE mnemonic to indicate the other possible causes of peripheral neuropathy.
Management
There is no cure or treatment to prevent it from progressing. Management is supportive, with input from various members of the multidisciplinary team:
- Neurologists and geneticists to make the diagnosis
- Physiotherapists to maintain muscle strength and joint range of motion
- Occupational therapists to assist with activities of living
- Podiatrists to help with foot symptoms and suggest insoles and other orthoses to improve symptoms
- Analgesia for neuropathic pain (e.g., amitriptyline)
- Orthopaedic surgeons for severe joint deformities
Last updated October 2023
